[Soil
Test Set Name]
Define the set name of soil
test to simulate.
[Method]
Select
the test that will be simulated. The test options available
are Tri-axial, Oedometer, CRS, DSS and General.
In
a triaxial test, stress is applied to a sample of the
material being tested in a way which results in stresses
along one axis being different from the stresses in perpendicular
directions. This is typically achieved by placing the
sample between two parallel platens which apply stress
in one direction, and applying fluid pressure to the specimen
to apply stress in the perpendicular directions.
With the triaxial test, it
is possible to test soil properties while controlling
the stresses applied in the vertical and horizontal directions
relative to the specimen.
Oedometer
test is designed to simulate the one-dimensional deformation
and drainage conditions that soils experience in the field.
To simulate these conditions, rigid confining rings are
used to prevent lateral displacement of the soil sample.
Porous stones are placed on the top and bottom of the
sample to allow drainage in the vertical direction.
With
the oedometer test, it is possible to define a one-dimensional
compression test for soil models.
In
a Constant Rate of Strain test (CRS test), it is possible
to gradually apply a load to a soil model by increasing
the displacement of a pressure cylinder at a constant
rate.
In
a CRS test, it is possible to gradually apply a load to
a soil model by increasing the displacement of a pressure
cylinder at a constant rate.
The
DSS test can be used to determine the shear strength of
a soil model.
The
general soil test can be used as a customisable soil test
mode. The user can define arbitrary stress and strain
conditions.
[Material]
Define
the soil material properties.
[Initial
Stress]
Define
the initial stress. In case of ‘General’ type, it is possible
to define the stresses of each direction.
[Boundary
Condition]
The
boundary condition is decided by the test method. In case
of ‘General’ type, it is possible to restrain the stress
/ strain conditions of each direction. This is an initial
condition which cannot be changed to the construction
stages (applies to all stages).
[Stage
Name]
Define
the different stages of the test.
[Advanced
Setting]
Define
the details for analysis.
[Analysis]
Start
the calculation for the selected soil tests.
[Show
Graph]
The
results of the test are displayed in the predefined diagrams
in the graph window.
Stage
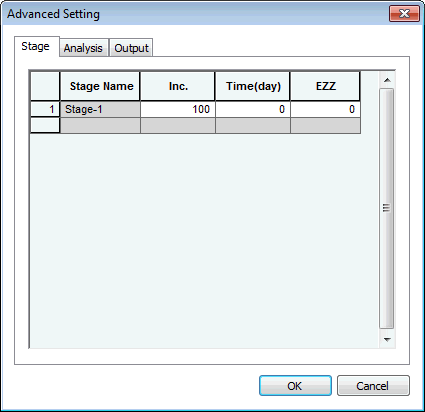
Each
stage is defined by a number of steps (Inc.), a duration
(in units of time) and a applied stress or strain increments.
The given stress or strain increment will be reached at
the end of the given duration in the given number of steps.
A negative stress or strain increment means additional
compression, whereas a positive stress or strain increment
means unloading or tension.
Analysis
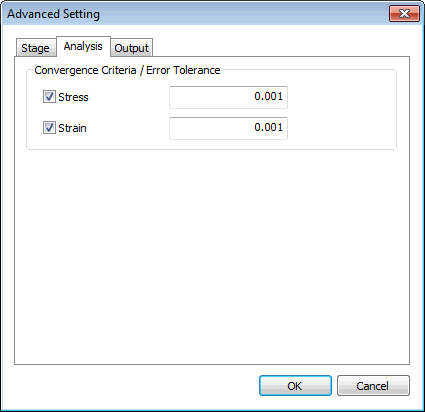
Define
the convergence criteria of analysis.
Output
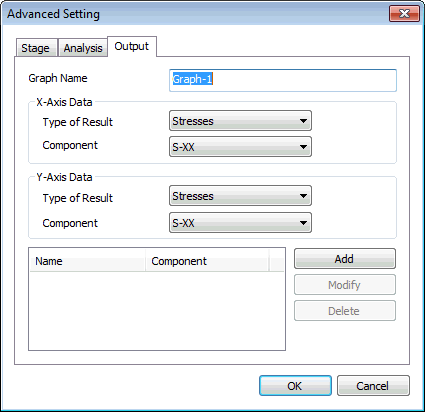
Define
the graph setting. You can select the configuration of
diagrams to display. |


